
Custom Online Sheet Metal Fabrication For Your Idea
On Demand Manufacturing
- Free DFM review in 12 hours
- ISO 9001:2015 certificated
- Fast Lead time 3 days
Our Custom Sheet Metal Fabrication Services
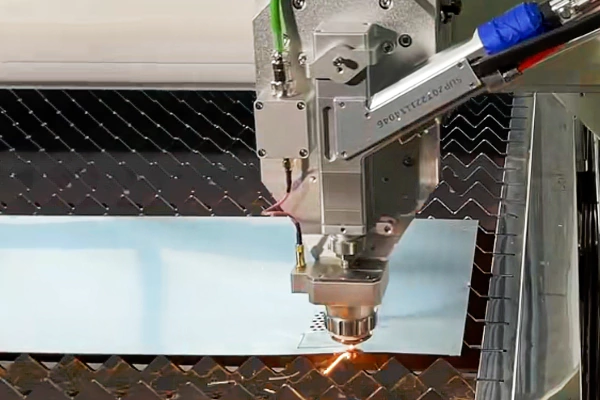
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting harnesses high-power lasers to precisely cut sheet metals, providing rapid processing and enabling the creation of intricate designs with smooth finishes and precise tolerances.
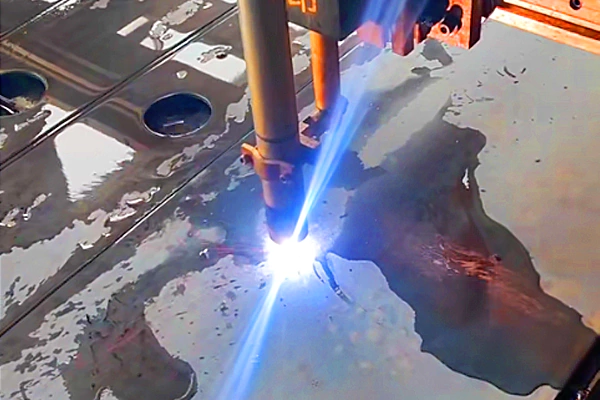

Plasma Cutting
Plasma cutting involves slicing through electrically conductive materials using a rapid jet of hot plasma. Particularly suited for thick materials, this method provides high-speed, cost-effective, and efficient solutions for large-scale industrial metal fabrication.
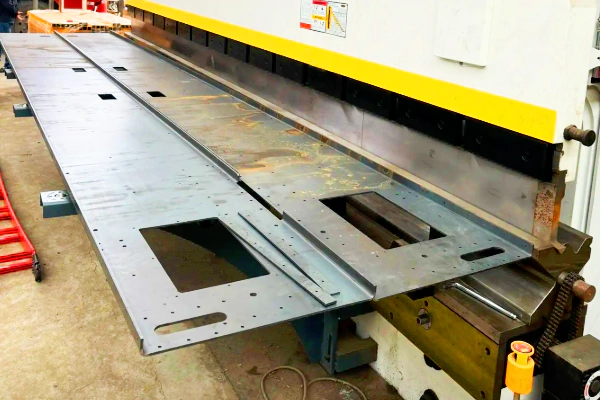

Bending
Bending, a flexible sheet metal fabrication technique, shapes materials into V-shapes, U-shapes, and channel shapes with remarkable precision and repeatability, requiring minimal setup costs. Ideal for intricate geometries.
How Ruiyi Works for you
Get Instant Quote
Upload your drawings to our quotation platform and we respond to most requests for quotations within 1 day.
Start Production
Once you place an order, we will start the production process, ensure the quality of the products, and keep you informed of production progress
Receive Your Parts
Fast air delivery and after-sales service follow up ensures order fulfillment.





Sheet Metal Fabrication Materials

Aluminum
Aluminum, prized for its lightweight yet sturdy properties, provides enhanced durability without adding unnecessary weight. Its exceptional malleability enables precise shaping, making it perfect for intricate designs.
Cooper
The benefits of copper are unmistakable: unmatched electrical conductivity, thermal efficiency, and inherent resistance to corrosion, guaranteeing longevity and optimal performance in various fabrications.
Stainless steel
Stainless steel, known for its durability and stain resistance, guarantees longevity and retains its appearance, even in challenging environments.
Cold Rolled Sheets
Cold rolled sheet is a product made from hot rolled coils that are rolled at room temperature below the recrystallization temperature.
Hot Rolled Sheets
The advantage of hot rolled sheet is that it is hot rolled at high temperature, which makes the grain of steel become finer and makes the steel structure stronger and tighter, with better ductility and stronger loading capacity.
Hot-dip galvanization Sheet
Hot-dip galvanized steel sheet is a kind of thin steel sheet which is immersed in a molten zinc bath to make a layer of zinc adhering to its surface. At present, the main use of continuous galvanizing process production, that is, the coil of steel plate continuous immersion in the molten galvanizing tank, made of galvanized steel;Sheet Metal Fabrication Processes
Design and draw the parts drawing of its sheet metal parts, also called three-dimensional view, its function is to express the structure of its sheet metal parts in the form of drawings.
That is to expand a complex structural part into a flat piece
There are many ways, the main ones are as follows:
a. Shearing machine cutting is to use the shearing machine to cut out the length and width dimensions of the unfolded diagram. If there are punching holes or corner cutting, then turn to the punch machine to punch holes and corner cutting to form.
b. Punch blanking is to use a punch to punch out the flat structure of the unfolded parts on the plate in one or more steps. Its advantages are short working hours, high efficiency, and can reduce processing costs. It is often used in mass production. arrive.
c. NC blanking. When NC blanking, you must first write a CNC machining program. That is to use programming software to write the drawn expansion diagram into a program that can be recognized by the NC CNC machining machine. Let it follow these programs step by step. On the iron plate, the structural shape of the flat piece is punched out.
d. Laser blanking. It uses laser cutting to cut out the structural shape of the flat piece on an iron plate.
Flanging is also called drilling. It is to draw a slightly larger hole on a smaller base hole, and then tap the hole. This can increase its strength and avoid slippage. It is generally used for thinner plates. For sheet metal processing, when the plate thickness is relatively large, such as plate thicknesses above 2.0, 2.5, etc., we can tap directly without flanging.
Generally, punch processing methods include punching and corner cutting, punching and blanking, punching convex bulges, punching and tearing, drilling holes and other processing methods to achieve the processing purpose. The processing requires corresponding molds to complete the operation. The processing of convex bulges There are convex hull dies, and tear forming dies for punching and tearing.
As far as our factory is concerned, the commonly used riveting methods include pressure riveting studs, pressure riveting nuts, pressure riveting screws, etc. The riveting method is generally completed by a punch or a hydraulic riveting machine, and is riveted to the sheet metal parts. superior
Bending is to fold 2D flat parts into 3D parts. The processing requires a folding machine and corresponding bending molds to complete the operation. It also has a certain bending sequence. The principle is to bend first without interfering with the next cut. , which will produce interference back-folding.
It is to weld multiple parts together to achieve the purpose of processing or to seam a single part to increase its strength. The processing methods generally include the following: CO2 gas shielded welding, argon arc welding, spot welding, robot Welding, etc. The selection of these welding methods is based on actual requirements and materials.
Generally speaking, CO2 gas shielded welding is used for iron plate welding; argon arc welding is used for aluminum plate welding; robot welding is mainly used when the materials are large and the welds are long, such as cabinet welding, robot welding can be used. It can save a lot of task time and improve work efficiency and connection quality.
Generally, there are phosphate coatings, electroplated colorful zinc, chromate, baking paint, oxidation, etc. Phosphate coatings are generally used for cold-rolled plates and electrolytic plates. Its main function is to coat a protective film on the surface of the material to prevent Oxidation can then enhance the adhesion of the paint.
Electroplating colorful zinc is generally used for surface treatment of cold-rolled plates; chromate and oxidation are generally used for surface treatment of aluminum plates and aluminum profiles; the selection of specific surface treatment methods is based on customer requirements.
The so-called assembly is to put multiple parts or components together in a certain way to make it a complete item.
What needs to be paid attention to is the protection of materials and no scratches or scratches. Assembly is the last step in the completion of a material. If the material cannot be used due to scratches or scratches, it will need to be reworked, which will waste a lot of processing time and increase the cost of the material. Therefore, special attention must be paid to the protection of the material.

Sheet Metal Fabrication near me
FAQ
What is sheet metal fabrication?
Sheet metal fabrication is the process of cutting, bending, and assembling metal sheets to create custom parts, products, or structures for various industries.
What types of sheet metal fabrication services do you offer?
We offer laser cutting, bending, punching, welding, stamping, and assembly services to meet your specific project requirements.
What materials do you work with?
We work with various materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, galvanized steel, and copper.
What thickness of sheet metal can you handle?
We can handle sheet metal thicknesses ranging from 0.5mm to 20mm, depending on the material and project requirements.
Can you provide custom designs and prototypes?
Yes, we specialize in custom sheet metal fabrication and can create prototypes based on your designs or assist with design optimization.
Do you offer surface finishes for fabricated parts?
Yes, we provide various finishing options, including powder coating, painting, anodizing, polishing, and plating.
What industries do you serve with sheet metal fabrication?
We serve industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, construction, medical, and consumer products.
What is your production capacity for sheet metal fabrication?
We handle both low-volume and high-volume production runs, ensuring flexibility for projects of all sizes.
How do you ensure quality in sheet metal fabrication?
We use advanced equipment, skilled technicians, and rigorous quality control processes, including inspections, testing, and certifications, to ensure top-quality results.
Do you offer international shipping, and what is your lead time?
Yes, we ship worldwide. Lead times typically range from 5–15 business days, depending on the project's complexity and volume.
