Table of Contents
Rapid prototyping is a relatively new but transformative development in modern manufacturing. The first commercial rapid prototyping machine entered the market in the late 1980s. Since then, the technology has evolved far beyond its initial scope and is now widely used across industries—not just for developing prototypes but also for producing small batches of production-quality parts. Even sculptors and artists have adopted rapid prototyping methods to create complex exhibitions and artworks.
What Is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping refers to a collection of manufacturing techniques used to quickly fabricate a physical model or part directly from a digital design, usually a 3D CAD file. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing—where material is removed from a solid block—rapid prototyping is primarily additive, building parts layer by layer.
Common Rapid Prototyping Techniques
Rapid prototyping encompasses a wide range of technologies, including:
Stereolithography (SLA)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
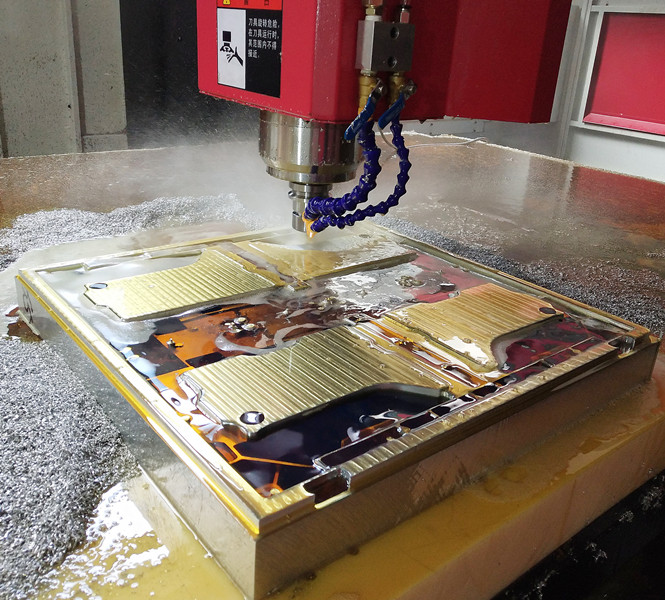
CNC Machining
Vacuum Casting / Cast Urethane
Solid Ground Curing (SGC)
Reaction Injection Molding (RIM)
Rapid Injection Tooling
Rapid Die Casting
Newer technologies such as ballistic particle manufacturing and 3D printing (three-dimensional printing) have also emerged and are gaining traction in both prototyping and small-batch production.
All these additive manufacturing methods start with nothing and gradually build up material to form a complete part. This contrasts with traditional subtractive approaches, such as milling or turning, where excess material is removed from a larger block.
Why Is Prototyping Important?
Skipping the prototyping phase can lead to costly and inefficient outcomes. Rapid prototyping offers many benefits that can help avoid design errors, reduce development time, and improve product functionality. Key advantages include:

1. Faster Time to Market
Rapid prototyping significantly shortens the product development cycle. Depending on the complexity of the part, time savings of 60% to 90% are achievable compared to conventional methods.
2. Design Validation and Iteration
Prototypes allow designers and engineers to:
Evaluate form, fit, and function
Identify design flaws early
Eliminate unnecessary features
Test usability with real users
This minimizes costly design changes after production has begun.
3. Improved Communication
A physical prototype serves as a tangible reference point, facilitating clearer communication among:
Designers
Engineers
Clients
Marketing and sales teams
It acts as a bridge between disciplines and improves cross-functional collaboration.
4. Better Requirement Definition
Traditional methods like interviews and focus groups often fall short because people find it hard to visualize a product before seeing it. A working prototype provides a concrete example to refine and validate requirements early in the process—greatly reducing the risk of costly rework.
5. Faster Conflict Resolution
Engineers often have different opinions on the best way to implement a feature. Prototypes allow teams to:
Test multiple approaches
Benchmark performance
Make data-driven decisions
This speeds up consensus and helps ensure the right design path is chosen.
6. Encouraging Honest Feedback
Low-fidelity or early-stage prototypes are easier for users to critique. If a prototype looks “unfinished,” users are more willing to provide candid feedback, which leads to a better final product.
Rapid Prototyping in China
Rapid prototyping began in China in the early 1990s and has seen explosive growth over the past two decades. Today, China is a global hub for prototyping services, with world-class companies emerging in key manufacturing regions.
Key Areas:
Shenzhen
Dongguan
Zhongshan
Guangzhou
These cities, located in the Pearl River Delta region, are at the forefront of China’s rapid prototyping industry.
Competitive Advantages:
Compared to other countries, China offers:
Significantly lower costs, especially for:
CNC machined prototypes
Vacuum cast parts
Reaction injection molded parts
Rapid tooling
Skilled labor and advanced infrastructure
Fast turnaround times
As innovation accelerates and global demand grows, China is poised to lead the next wave of the rapid prototyping revolution.
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping is no longer just a tool for testing concepts—it’s a cornerstone of modern product development. By enabling faster iteration, better collaboration, and early error detection, it helps companies bring better products to market, faster and more affordably.
With its advanced capabilities and cost efficiency, China has become one of the most attractive destinations for rapid prototyping, providing global companies with the speed and precision they need to succeed in competitive markets.