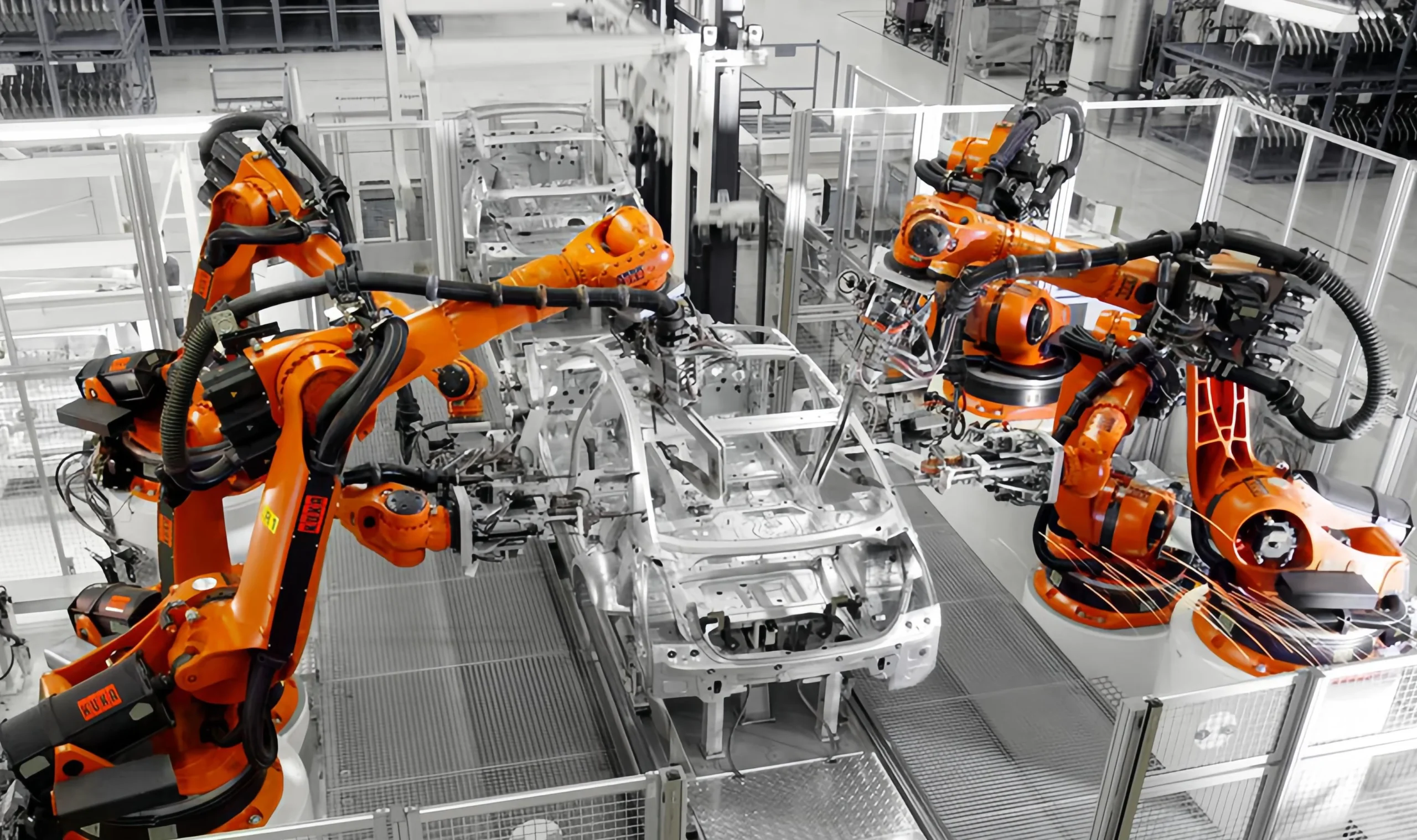
Automotive machining has evolved from manual to intelligent, automated processes. Early machining relied on manual labor and rudimentary machine tools, resulting in low efficiency and limited precision.
CNC technology has significantly enhanced machining accuracy, enabling the mass production of automotive engines, transmissions, and chassis parts.
Advanced technologies like 5-axis machining, 3D printing, and smart automation enhance automotive machining, improving efficiency, quality, and sustainability.
These advancements propel the automotive industry toward continuous progress in high performance, low energy consumption, and sustainability.
Overview of Automotive Machining Technology
Automotive machining shapes raw materials into functional components. Primary machining methods include turning, milling, drilling, boring, grinding, planing, broaching, sawing, tapping and threading, and electrical discharge machining (EDM).
Information technology and CNC automation have greatly improved machining efficiency and precision.
To better grasp the significance of emerging technologies, it is essential to examine the developmental trajectory of automotive machining.
Development of Automotive Machining Technology
Current trends primarily focus on high-speed machining technology, process integration, and streamlined workflows. High-speed machining Technology advances thanks to breakthroughs in cutting tool and machine tool technologies.
Process integration in automotive manufacturing replaces traditional grinding, milling, and broaching with turning, extrusion, rolling, or multi-edge tooling methods.
Process Simplification utilizes composite machining technology to reduce intermediate steps, streamline production workflows, and enhance manufacturing flexibility.
Impact of Machining Technology Development on Automotive Manufacturing
The application of machining technology has a profound and extensive influence on automotive manufacturing. We can broadly categorize its impact as follows:
Enhanced efficiency:
CNC machines and industrial robots automate the automotive manufacturing process, optimizing operations and reducing production cycles.
Enhanced precision:
Machining technology and CNC control ensure high-accuracy production of complex automotive parts like engine blocks and crankshafts.
Improving quality:
Surface treatments enhance the finish, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance of automotive components.
Advanced automotive technologies drive industry upgrades and the production of key components for new energy vehicles.
Application of Machining in Automotive Manufacturing
Machining is a fundamental process in automotive manufacturing, providing the precision and consistency required to produce complex parts with high performance and reliability.
From molds and engine components to structural parts, machining ensures dimensional accuracy and surface quality that meet strict industry standards.
With advancements in digital manufacturing and process optimization, modern machining technologies have become more efficient, flexible, and intelligent.
Among these, cutting technology plays a central role in shaping automotive components.
Cutting Technology
One application of cutting technology is in automotive mold manufacturing and processing.
Cutting technology uses process models to optimize tool selection, feed rates, and parameters, enhancing efficiency and precision.
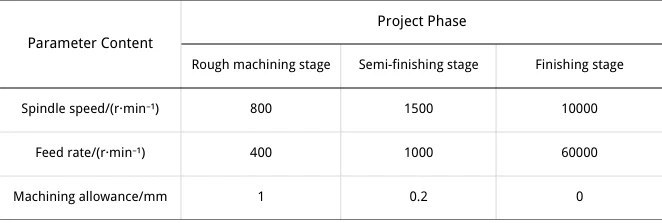
For an automotive interior mold, optimizing cutting parameters maximizes process efficiency.
Table 1: Rough machining uses high feed and cutting rates with circular paths, 800 rpm spindle, 400 mm/min feed, and 1 mm allowance.
Semi-finishing uses small feed and cutting rates to remove burrs while leaving 0.2 mm allowance; spindle speed is 1500 rpm, feed rate 1000 mm/min.
Finishing grinds the mold with ultra-low feed for stable control; spindle 10,000 rpm, feed 60,000 mm/min, 0 mm allowance.
Fixture Technology
In automotive manufacturing, fixtures position workpieces; their accuracy must exceed that of the workpiece, and rigidity ensures quality and precision.
Fixtures made from 40–60 mm steel: China produced 60 million in 2020, using 43 million domestically and exporting 17 million.
To enhance fixture quality and optimize performance, manufacturers should control raw material selection and conduct structural R&D.
Fixture design ensures process rationality by setting positions, quantities, and including positioning and support modules.
Use rigid, lightweight aluminum fixtures and follow cleaning and anti-rust specs to extend life.
Adjust fixture components to ensure clamping, positioning, and support meet design specifications.
During inspection, verify clamping force and check fixture surface for flatness, scratches, and burrs to ensure standardization and stability.
Implement dynamic maintenance management for fixtures, conducting regular inspections and upkeep to ensure fixture stability.
Industrial Robots
Industrial robots are multi-jointed arms that execute tasks automatically and, with AI, can operate using customized instructions.
Robots in industrial settings can carry out a wide range of processing and manufacturing tasks, with broad applications across manufacturing and other sectors.
Industrial robots enhance production capabilities and optimize processes, proving especially valuable in automotive manufacturing.
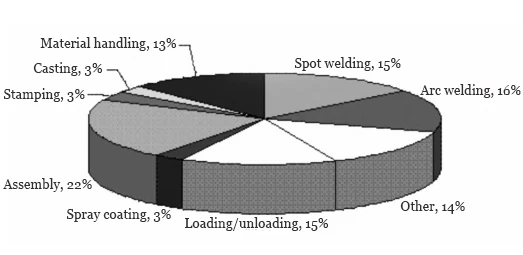
Data indicates the following usage proportions of industrial robots in the automotive industry:
Assembly: 22%, Arc Welding: 16%, Spot Welding: 15%, Loading/Unloading: 15%, Material Handling: 13%, Casting: 3%, Stamping: 3%, Painting: 3%, Other: 14% (see Figure 1).
Welding robots, robust and efficient, perform ~4,000 welds per vehicle in automotive manufacturing (Figure 2).
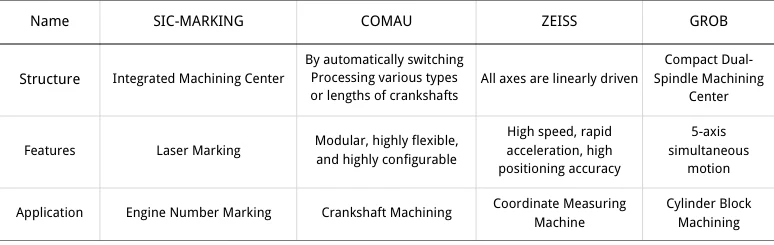
Growing automotive demand drives industrial robots: SIC-MARKING marks engines, COMAU handles crankshafts, ZEISS measures, and GROB machines cylinder blocks (Table 2).

Case Study Analysis
To better illustrate the practical applications of machining technologies in automotive manufacturing, we examine representative case studies.
These cases highlight how machining principles are applied to real components, demonstrating their impact on efficiency, precision, and product performance.
The following sections analyze specific parts, beginning with the engine crankshaft, a core component that directly influences overall engine reliability and power output.
Engine Crankshaft Structure and Machining Characteristics
The crankshaft converts pistons’ reciprocating motion into rotational torque, The flywheel transmits it to the transmission and auxiliary components.
As a critical engine component, the crankshaft must possess adequate rigidity and strength. Based on material, crankshafts fall into four categories:
steel crankshafts, cast iron crankshafts, ductile iron crankshafts, and aluminum alloy crankshafts.
Cast iron crankshafts suit low-power engines, ductile iron for small to medium engines, and aluminum alloy for sports or compact engines.
Crankshaft quality directly affects engine performance; manufacturing must follow specifications and consider crankshaft characteristics.
A crankshaft comprises multiple crankpins, each consisting of one connecting rod journal, two cranks, and two crankshaft journals, as illustrated in Figure 3.
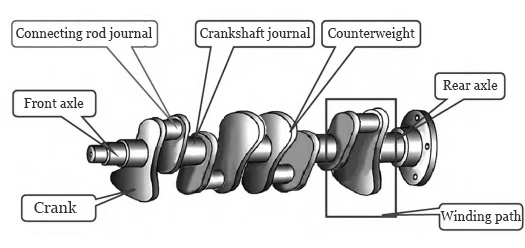
Crankshaft machining involves multiple surfaces, each with strict dimensional and geometric tolerances; out-of-spec workpieces require re-machining.
Long-neck crankshafts occupy space, and low rigidity can cause wear, deformation, and reduced engine quality.
Eccentricity between the main and connecting rod journals requires precise design to prevent dimensional errors.
Analysis of Crankshaft Machining Process
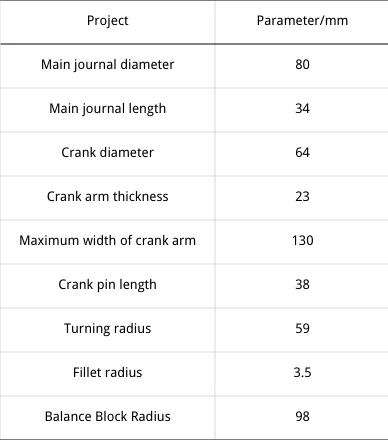
Manufacturers use modern techniques in crankshaft manufacturing. Table 3 shows parameters for a four-stroke vertical inline water-cooled engine crankshaft.
Step 1: Analyze the machining process.
The crankshaft end faces and center bore are machined using specialized machines and fixtures through face milling and center drilling.
Operators grind the main journals and connecting rod journals sequentially. After finishing the main journals, they mill the keyway.
Step 2: Select a blank manufacturing method:
45 steel with good toughness and rigidity is forged to ensure crankshaft durability.
Step 3: Select the machine tool.
Machine selection must consider the crankshaft’s dimensions and precision requirements.
The C620-1 horizontal machining lathe is chosen for this project.
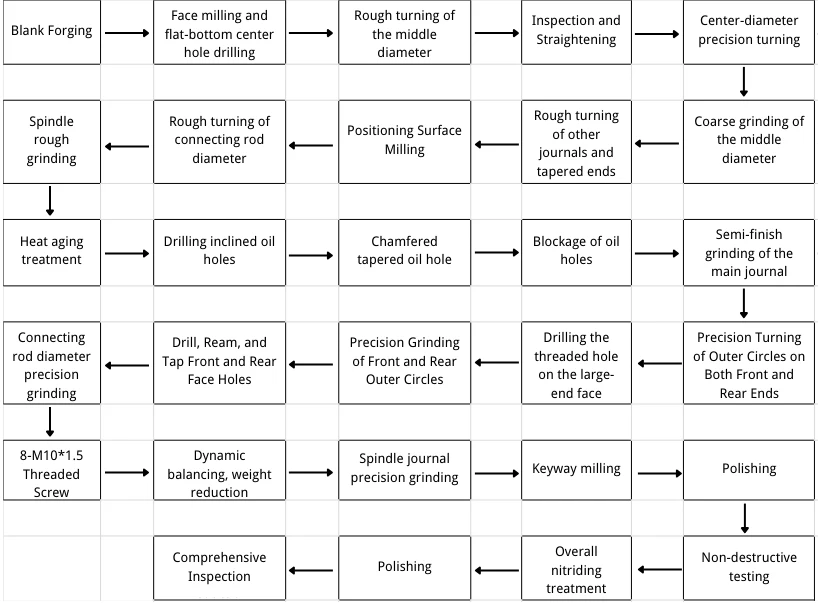
Step 4: Determine the process route.
The machining process route for this project is shown in Figure 4.
Step 5: Determine machining allowances.
Common methods include calculation, empirical estimation, and reference tables.
Step 6: Establish process dimensions and tolerances.
These are calculated based on the Concise Handbook of Mechanical Manufacturing Process Design.
Conclusion
Continuous innovation in mechanical technology presents development opportunities for the transformation, upgrading, and industrial advancement of China’s automotive manufacturing sector.
As machining technology evolves toward intelligent solutions, the comprehensive application of industrial robots, and network technology drives the integration of machining with positioning and image processing technologies—establishing positioning monitoring platforms—machining techniques can be applied scientifically, effectively, and systematically.
This fully leverages the advantages of automation technology to create scientific, efficient automotive production lines and ensure the stability of machining processes.
FAQ:
Answer: Automotive machining involves shaping raw materials into functional vehicle components through processes like turning, milling, drilling, and EDM. It is essential for producing high-precision engines, transmissions, and chassis parts, ensuring efficiency, quality, and reliability in modern automotive manufacturing.
Answer: Automotive machining has progressed from manual operations with low efficiency and precision to intelligent, automated processes using CNC technology, industrial robots, and advanced methods like 5-axis machining and 3D printing. This evolution allows high-accuracy mass production and streamlined workflows.
Answer: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology automates machining operations, greatly improving precision and efficiency. It enables consistent production of complex automotive components, reduces human error, and supports high-speed, high-volume manufacturing.
Answer: Primary methods include turning, milling, drilling, boring, grinding, planing, broaching, sawing, tapping, threading, and electrical discharge machining (EDM). These techniques are selected based on component geometry, material, and tolerance requirements.
Answer: Cutting technologies use process models to select appropriate tools, feed rates, and cutting parameters. This optimization improves efficiency, accuracy, and surface quality, as demonstrated in roughing, semi-finishing, and finishing stages for automotive interior molds.
Answer: Fixtures accurately position workpieces and ensure rigidity during machining, which directly impacts quality and precision. Proper fixture design, material selection, and maintenance enhance manufacturing stability and reduce errors in high-volume automotive production.
Answer: Industrial robots perform assembly, arc welding, spot welding, loading/unloading, material handling, casting, stamping, and painting tasks. They increase productivity, consistency, and precision, with welding robots performing up to 4,000 welds per vehicle in modern automotive plants.
Answer: Crankshafts are critical engine components that convert pistons’ reciprocating motion into rotational torque. Manufacturing involves selecting high-strength materials, precision machining of multiple journals, maintaining tight dimensional tolerances, and using specialized machines, fixtures, and process routes to ensure durability and performance.
Answer: Emerging trends include high-speed machining, process integration, 5-axis machining, 3D printing, and smart automation. These innovations streamline workflows, enhance precision, reduce energy consumption, and support sustainable, high-performance automotive production.
Answer: Modern machining technologies, combined with CNC automation, industrial robots, and optimized fixtures, improve production efficiency, ensure high-precision components, enhance surface quality, and reduce waste. This drives sustainable practices while maintaining high-performance automotive standards.