Table of Contents
What is Sandblasting?
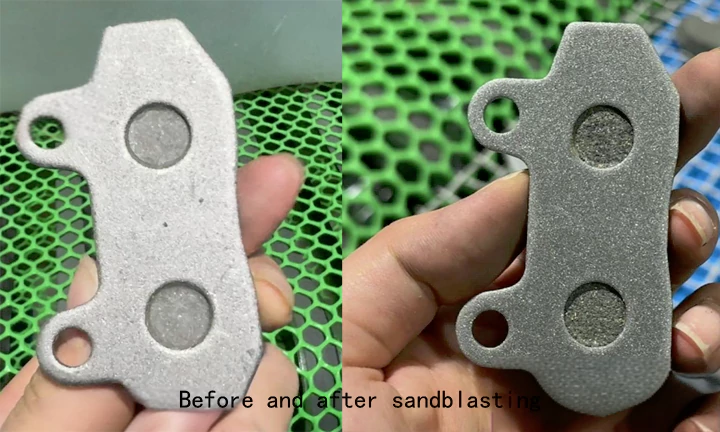
Sandblasting is a widely used surface treatment technique in the machining and prototyping industries.
It involves propelling high-speed abrasive particles (such as sand, glass beads, or steel balls) against a workpiece surface to remove impurities, smooth rough areas, and enhance aesthetics.
Beyond cleaning and deburring, sandblasting also creates matte or textured finishes ideal for decorative or functional applications.

Core Applications of Sandblasting
Silicone Mold Sandblasting
Sandblasting removes visible tool lines from silicone molds, helping prevent rust while achieving a smooth, clean surface for higher-quality mold performance.
Fine Etching for Plastic Molds
This technique engraves fine textures or bumps into plastic molds, enhancing their decorative appeal and tactile effect.
Pre-Oxidation Surface Treatment
Before oxidation, sandblasting evens out metal surfaces and creates a uniform texture, improving the appearance and consistency of the oxidized finish.
Handpiece Surface Refinement
In handpiece manufacturing, sandblasting removes burrs, paint, and tool marks. This significantly improves surface quality, ensuring consistency, smoothness, and a refined look.
Broad Scope of Sandblasting Applications
Sandblasting is suitable for various materials beyond metal, including plastics, glass, and ceramics. Common applications include:
Metal Rust and Scale Removal
Sandblasting completely eliminates rust, oxides, and surface contaminants from metal, restoring its original shine and boosting corrosion resistance.
Aluminum Alloy Treatment
Used in aerospace and automotive industries, sandblasting enhances the corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetics of aluminum alloy parts.
Decorative Glass Finishing
Sandblasting creates matte textures on glass surfaces, widely applied in architecture and luxury appliances for a frosted, stylish effect.
Plastic Deburring
Plastic parts benefit from sandblasting, which removes burrs and leftover mold residue for a smoother, polished finish.
Acrylic Surface Texturing
Sandblasting introduces a matte effect to acrylic, reducing glare and enhancing appearance, especially for display and lighting components.
Polycarbonate (PC) Enhancement
Common in automotive and lighting applications, PC sandblasting improves surface uniformity and decorative appeal.

Choosing the Right Sandblasting Material and Process
The choice of blasting material significantly affects the final surface effect. Matching the right abrasive to the workpiece material and desired finish is essential.
1. Acrylic Sandblasting
High Haze, Strong Atomization:
Use glass sand or white corundum. Their high friction creates a coarse texture and excellent diffusion of light.Low Haze, High Transparency:
Glass beads are ideal. Their finer grains preserve transparency while creating a soft matte finish. For enhanced translucency, a small mix of glass sand can be added.
2. Stainless Steel Sandblasting
Material Matching:
For polished or tensile-finished alloy steel, choose abrasives based on surface conditions.For Rough Finishes:
Use brown or white corundum for aggressive surface texture.For Smooth Finishes:
Opt for glass beads or fine glass sand for delicate, uniform surfaces.
3. Die Casting & Low Alloy Steel Treatment
Shot Blasting with Cast Steel Balls:
Shot blasting machines use steel balls to efficiently clean die-cast parts, removing rust and surface contamination.Aluminum Alloy Brightening:
To achieve a clean, white surface, stainless steel or steel wire shot is preferred. For cost efficiency, mix cast steel balls with continuous steel shot for balanced results.

Conclusion
Sandblasting is a powerful, versatile surface treatment method essential for improving the visual and functional quality of a wide range of materials. From metal to plastic to glass, selecting the right sandblasting technique and material ensures optimal results.
Whether you aim for smooth finishes, improved corrosion resistance, or decorative effects, the right choices in sandblasting can significantly elevate your product’s value and performance.
FAQ:
Sandblasting is a surface treatment process where high-speed abrasive particles (like sand, glass beads, or steel balls) are blasted onto a workpiece to remove impurities, smooth surfaces, and enhance appearance or functionality.
Sandblasting is suitable for metal, plastic, glass, ceramics, and more. It's widely used in industries like aerospace, automotive, mold making, and decorative finishing.
Key uses include:
Rust and oxide removal from metal
Texturing surfaces for decoration
Deburring plastic components
Preparing surfaces for oxidation or coating
Refining silicone and plastic molds
It removes visible tool lines, burrs, and surface imperfections, improving surface finish, reducing rust risk, and enhancing the visual and tactile quality of molded parts.
Sandblasting evens out the surface, creating a uniform texture that allows oxidation layers to form consistently and improves the final appearance and durability of the treated metal.
Sandblasting gives acrylic a matte, anti-glare look and adds frosted, decorative textures to glass—ideal for displays, lighting, and luxury architectural elements.
Glass beads for smooth, soft matte finishes
White/brown corundum for rough, aggressive texturing
Steel shot for heavy-duty cleaning and metal brightening
Glass sand for high haze or strong atomization on acrylic
Sandblasting uses finer abrasives for surface refinement, while shot blasting (often with steel balls) is more aggressive and typically used for cleaning die-cast or low alloy steel parts.
In aerospace and automotive industries, sandblasting improves corrosion resistance, ensures a uniform look, and increases the durability of aluminum alloy components.
Choosing the correct abrasive ensures the desired surface texture, optical effect, and material protection. Using the wrong one can lead to over-processing, poor aesthetics, or even surface damage.