With the continuous development of the modern manufacturing industry, laser cutting technology has become increasingly prominent.
This is especially true in the field of sheet metal manufacturing, where it has seen a large number of applications.
Therefore, the manufacturing industry and technical personnel must be clear about the basic situation of laser cutting technology and its main types.
Then, based on this understanding, they should combine it with the actual manufacturing materials and apply the corresponding laser cutting technology in a reasonable manner.
Laser cutting technology can fully exploit its technical advantages.
It can meet the actual production and processing needs of the manufacturing industry.
It also promotes the use of laser cutting technology. Additionally, it contributes to the synergistic development of the modern manufacturing industry.

Overview of laser cutting technology
1. Basic introduction
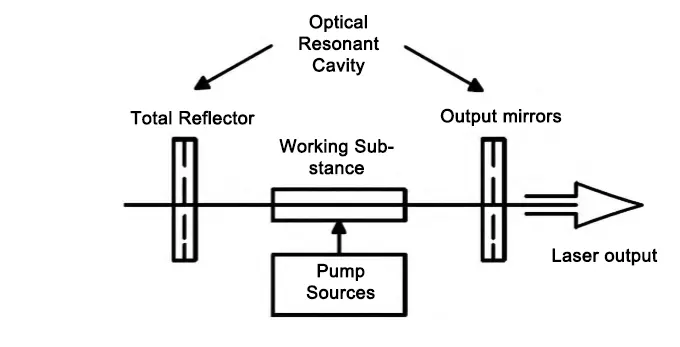
Laser cutting technology involves using a high-power density laser beam to cut material, which rapidly vaporizes, ablates, melts, or reaches its ignition point, evaporating to form tiny holes.
At the same time, with the help of the laser beam coaxial auxiliary high-pressure gas, the molten material will be blown off.
As the laser beam moves, the hole continuously forms a narrow slit, thus completing the cutting of the processed material.
Figure 1 illustrates the fundamental principle of laser cutting technology.
The main advantages of this technology include high cutting quality, high cutting efficiency, fast cutting speed, the ability to process material without direct contact, and strong applicability.
Modern manufacturers widely utilize laser cutting technology due to its numerous advantages.
2. Application Status
Manufacturers widely utilize laser cutting technology in today’s industry, particularly in mechanical production, because it is highly adaptable and can cut and process a wide range of materials.
From the point of view of cutting materials, laser cutting technology has three main application directions:
One is for cutting metal materials. Two are for cutting non-metallic materials. There are three for cutting other materials.
Laser cutting technology demonstrates significant advantages regardless of the material being cut.
Therefore, the development prospects of laser cutting technology are also vast in the modern manufacturing industry.
Main types of laser cutting technology
1. Vaporization cutting technology
Manufacturers most widely use vaporization cutting technology in laser cutting applications.
When the technology applies a high-power-density laser beam irradiation to the surface of the material to be cut,
A small amount of the laser will be reflected. Most of the laser will be absorbed by the laser cutting surface.
The surface temperature of the cut material will quickly reach its boiling point, causing the vaporization of the cutting part of the material.
This process results in the formation of small holes.
At the same time, under the influence of surface oxidation, etc., the ejected steam will carry away most of the molten material and ultimately form a very narrow vaporization incision on the cutting surface.
This technology is usually realized with the help of a pulsed laser, and its main application is the cutting of wood, ceramics, plastics, and other non-melting materials.
2. Melting cutting technology
Melting cutting is also a type of laser cutting technology. In specific applications, this technology requires relatively high laser power.
Compared with vaporization cutting technology, this method removes the melted material not through vaporization but by using auxiliary gas to blow it away.
With this cutting technique, the laser beam ignores vapor during the process and interacts only with the material in front of it as it moves through the kerf gap.
Additionally, the laser power density used in this cutting mode is relatively low.
The laser beam will form a sizeable beveled shooting angle on the transmission surface of the material during cutting.
This results in the cutting surface not absorbing enough laser energy to meet the needs for continuous melting.
Therefore, the melting process should be carried out gradually. The final cutting will form a wave-shaped pattern.
This cutting technology is particularly suitable for materials that can undergo an exothermic reaction with oxygen, such as copper and aluminum.
In the blowing off of the melted material, the commonly used auxiliary gases are mainly inert gases of various types.
3. Reaction melting cutting technology
Reaction melting cutting uses a laser beam to heat the surface of the cut material or workpiece.
This heating raises the surface temperature to the ignition point. Then, industrial pure oxygen is applied to react with the processed material, releasing a large amount of heat.
Ultimately, this process forms a molten oxide at the location of the seam.
When auxiliary gases blow off the molten oxides, the neighboring materials absorb some of the heat, causing their temperature to gradually increase.
When the temperature reaches the ignition point, a combustion reaction occurs, releasing additional heat.
In this way, the reaction-melting cutting process can continue continuously.
Compared with the first two laser cutting technologies, this cutting technology applies laser power density lower, usually only 1/20 of the vaporization cutting technology.
In the current machinery manufacturing field, this laser cutting technology is mainly used for cutting materials such as titanium and steel.
Specific applications
With the application and development of laser cutting technology, this technology has an increasingly wide range of applications in the modern manufacturing industry.
It also reflects increasingly significant application advantages. Currently, the laser cutting technology in the manufacturing industry is mainly applied in the following directions.
Metal material processing
In the modern manufacturing industry, metal material processing can significantly improve its efficiency.
It can also reduce processing costs through the reasonable application of laser cutting technology.
This can also further improve the processing accuracy of metal materials, resulting in more precise products.
However, due to the technology’s limitations, it is only applicable to the cutting and processing of sheet metal and is not relevant to the processing of thick sheet metal.
Regarding the current manufacturing cutting processing plant, carbon dioxide laser is the most commonly used laser cutting equipment.
Its 2 kW output power allows it to quickly cut 8 mm below the thickness of stainless steel and 12 mm below the thickness of ordinary carbon steel.
This technology and equipment can significantly improve the efficiency of metal material cutting and processing when applied reasonably.
Additionally, it helps reduce material loss in processing and results in higher-quality processed products.
Compared to traditional cutting and processing technology, laser cutting technology produces and processes finished materials more closely in line with design standards.
Under normal circumstances, its positioning accuracy can be controlled at 0.05 mm, and its repeat positioning accuracy at 0.02 mm.
Therefore, with the continuous development of the manufacturing industry, the
Therefore, with the continuous development of the manufacturing industry, the application of laser cutting technology in the field of metal materials processing is becoming increasingly extensive.
It is gradually becoming one of the essential processes in modern manufacturing.
This will also further promote the manufacturing industry to high-end, digital, and intelligent transformation and development.
Non-metallic material processing
In addition to being more applicable in the manufacturing industry for processing metal materials, laser cutting technology is also well-suited for processing non-metallic materials.
In today’s manufacturing, laser cutting technology processes synthetic and organic non-metallic materials, including cutting applications.
Compared to metal materials, non-metallic materials have a higher absorption rate of laser energy.
Therefore, applying laser cutting technology to cutting and processing achieves higher efficiency than when processing metal materials.
Therefore, laser cutting technology is also widely used in non-mechanical product cutting and processing, such as cutting watch gemstones on the shaft hole, processing non-metallic templates, and so on.
In the laser cutting process of these materials, the processing gases used for different non-metallic materials vary. The non-metallic materials and cutting parameters for laser cutting are presented in Table 1.

Laser cutting technology in non-metallic materials can be effectively applied by reasonable control of the above processing parameters.
This approach ensures maximum processing efficiency and accuracy, producing higher-quality products.
Additionally, it helps realize overall production and processing cost control.
It is the only way to ensure that laser cutting technology is well applied in the processing of non-metallic materials.
Mechanical mold processing
Laser cutting technology in machinery, mold production, and manufacturing primarily manifests in two major directions.
The first direction is its use in producing stacked molds made of steel.
The second direction is its application in forming thin plate-stacked three-dimensional molds.
For steel plate system stacked mold cutting processing, the staff can follow the model design standards.
Using laser cutting technology, they can perform high-precision cutting on steel plates with a thickness of no more than 6 mm.
This ensures the completion of the entire stacked mold production and processing.
After practical application, it is found that the economic cost of this technology in manufacturing steel plate laminated molds is only about one-third of that of the ordinary mechanical processing mode, resulting in significant economic benefits.
At the same time, the molds processed by this technology also have very high precision; their accuracy can generally be controlled at ± 0.01 mm.
For thin plate stacked into a three-dimensional mold, laser cutting, the operator can use computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) and other software combination of processing.
This method effectively ensures the accuracy of production and processing for such mechanical molds, while also reasonably simplifying their design and manufacturing process, resulting in higher production and processing efficiency.
Direction of development
Although laser cutting technology has been widely adopted in the modern manufacturing industry, offering significant application advantages, its development continues to progress.
As production and processing technology requirements continue to improve, the application of laser cutting technology also requires further development.
Through the practical application of laser cutting technology in the current manufacturing industry, certain shortcomings have been identified.
One such limitation is the restriction on material thickness. Laser cutting technology is not effective in cutting and processing materials with thicknesses exceeding a certain limit.
Laser cutting equipment is expensive, making it unaffordable for some small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises.
As a result, its promotional effect is not ideal. Additionally, laser cutting technology has not yet established a robust connection with many current advanced technologies.
Furthermore, the overall operation and control of this technology still have significant room for improvement.
Developed directions
Based on this, in the future development of the manufacturing industry, laser cutting technology should be developed in the following directions:
(1) to take reasonable methods and measures to improve the laser cutting ability continuously so that it is more adaptable in the thickness of the material, to expand its scope of application constantly;
(2) The cost of laser cutting equipment can be effectively reduced through reasonable technical improvements.
Supporting hardware and software enhancements play a crucial role in achieving this cost reduction.
By lowering costs, laser cutting technology can be widely adopted by more manufacturing enterprises.
This will ultimately lead to a more ideal application and promotion effect.
(3) Modern big data technology, automation technology, and intelligent technology should be integrated into laser cutting technology in practice.
Based on this integration, corresponding information technology, automation, and intelligent laser cutting control systems can be developed.
This approach will enhance the level of information technology, automation, and intelligent control in laser cutting.
As a result, it will maximize control effectiveness, processing efficiency, and product quality.
In this way, we can make laser cutting technology in the modern manufacturing industry to play a better application advantages, and with the modern manufacturing industry, towards a more advanced direction.
Conclusion
In today’s manufacturing industry, laser cutting technology has significant advantages for application.
Based on this, relevant enterprises, researchers, and staff must strengthen the study of laser cutting technology.
They should understand its basic principles, main functions, and current applications.
By considering the actual production and processing needs of modern manufacturing, they can reasonably introduce laser cutting technology.
At the same time, it should be based on the manufacturing industry’s future development goals to take a reasonable approach to the innovation of laser cutting technology so that it moves in a better direction.
In this way, laser cutting technology will have better application advantages in the manufacturing field.
It can meet the actual production and processing requirements for various materials and workpieces in the manufacturing industry.
This enables the synergistic and sustainable development of laser cutting technology and modern manufacturing.
FAQ:
What is laser cutting technology and how does it work?
Laser cutting technology uses a high-power density laser beam to heat materials to their melting, vaporization, or ignition point. It then uses auxiliary gases to blow away molten material, forming a narrow slit and completing the cut.
What are the main types of laser cutting techniques?
The three main types are:
Vaporization cutting: Material is vaporized using a high-power laser.
Melting cutting: Uses laser and gas to melt and blow away material.
Reaction melting cutting: Involves combustion with oxygen to assist cutting.
What materials can be cut using laser cutting technology?
Laser cutting is suitable for a wide range of materials, including:
Metal materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, titanium
Non-metallic materials such as ceramics, plastics, wood, and synthetic materials
Specialty materials used in mechanical molds and watch components
What are the advantages of laser cutting over traditional cutting methods?
High cutting precision
Clean and narrow cuts
Minimal material waste
No physical contact with the workpiece
Fast processing speeds
Strong adaptability to different materials
What are the limitations of laser cutting technology?
Difficulty cutting thick materials
High initial equipment cost
Limited accessibility for small to medium-sized businesses
Need for better integration with modern automation and control systems
In which industries is laser cutting most commonly used? Laser cutting is widely used in:
Sheet metal fabrication
Mechanical manufacturing
Mold making
Watch and precision part industries
Automotive and aerospace sectors
What gases are used in laser cutting processes?
The gases vary based on material and technique:
Oxygen for reaction melting (oxidation cutting)
Inert gases (like nitrogen or argon) for melting and vaporization cutting
Specific gases are selected to aid cutting and reduce oxidation or contamination.
How does laser cutting benefit non-metal material processing?
Non-metal materials absorb laser energy better, leading to:
Higher cutting efficiency
Greater precision
Lower thermal distortion
Wider application in non-mechanical industries
How is laser cutting used in mechanical mold production?
Laser cutting allows high-precision shaping of laminated steel molds and 3D thin-plate molds. It reduces production costs and improves accuracy to ±0.01 mm, especially when combined with CAD/CAM software.
What are the future directions for laser cutting technology?
Improving cutting capacity for thicker materials
Lowering equipment costs for broader accessibility
Integrating with automation, big data, and intelligent control systems
Enhancing control, efficiency, and product quality in smart manufacturing



