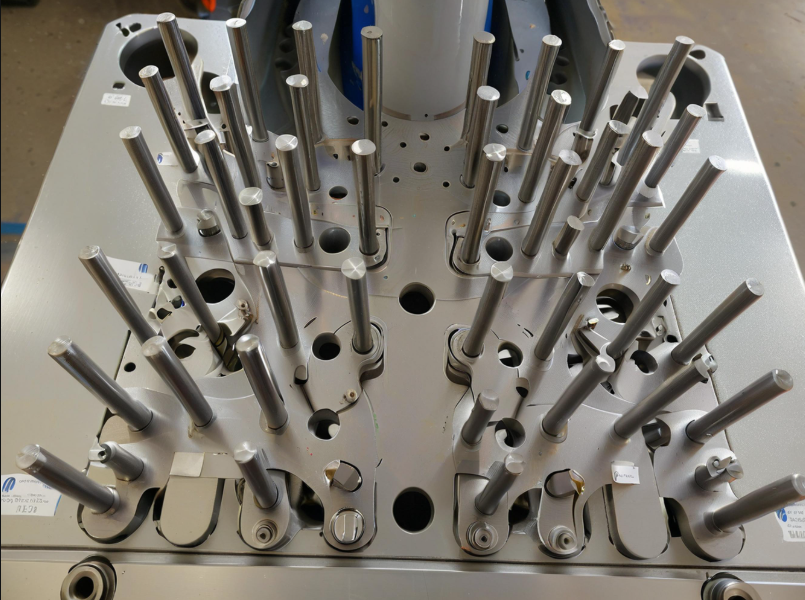
Zinc alloy die-casting is based on zinc alloy material, which is die-casting by high temperature injection and low temperature cooling.
It forms alloy die-casting products of various shapes. Zinc alloy die-castings have large specific gravity, good casting performance and bright surface.
It can also perform various surface treatment processes such as plating and spraying.
Zinc alloy materials have low melting points and are easily die-cast into a variety of shapes. And zinc alloy die-castings have better mechanical properties and wear resistance.
In the manufacturing process, the die casting process of zinc alloy die castings has special characteristics and advantages.
Advantages of zinc alloy die-casting.
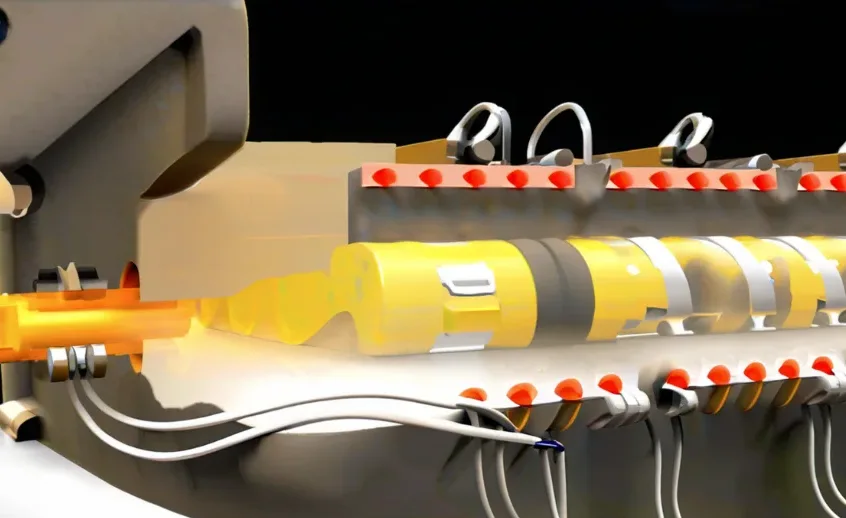
Die casting is a method that needs to be designed to use high pressure to push molten metal into the mold cavity. Non-ferrous metals such as zinc include copper, lead, magnesium, tin and other materials and are used for die casting of zinc alloy die castings.
This process is most suitable for the production requirements of small and medium-sized parts for mass production. This process is very convenient, thus becoming a widely used casting method for zinc metal processing business.
In the production of zinc alloy die castings, a different shape is required, from the simplest to the most complex designs are suitable. Compared to other processes, casting is more appropriate.
For the production of zinc width measuring part mixtures, this technology has created smooth surfaces for die castings as well as good dimensional accuracy and recognition. The thickness of the die casting is thinner than that of sand casting and metal casting.
Through this manufacturing process, relevant design factors can be set for threaded inserts, heating elements and high-strength bearing surfaces.
This technique also effectively reduces or eliminates the need for secondary operations.
Another characteristic exhibited during the zinc alloy die casting process is that it has the advantages of fast production speed and high tensile strength.
Die casting is a tool that uses a system to perform die casting in a fast cycle time and with metals that can be used in the molten state.
In the die casting process, two types of die casting machines are used, including hot chamber die casting machines and cold chamber die casting machines.
Advantages
The zinc alloy die casting process offers several key advantages, making it a popular choice in various industries like automotive, electronics, hardware, and consumer products. Here’s a breakdown of its main advantages:
Excellent Dimensional Accuracy
Zinc alloys allow for tight tolerances and complex geometries.
High repeatability and minimal need for post-machining.
Suitable for thin-wall parts.
Superior Surface Finish
Smooth surface finish (Ra ≤ 1.0 μm) right out of the mold.
Easy to plate, paint, or powder coat for cosmetic parts.
Ideal for decorative components like handles and logos.
High Strength and Toughness
Better impact resistance than aluminum or magnesium die castings.
Suitable for structural parts requiring good mechanical strength.
Good wear and abrasion resistance.
Low Melting Point (≈ 380–420°C)
Lower energy consumption during casting.
Longer mold life compared to aluminum or magnesium die casting.
Reduced tool wear and production costs.
Excellent Castability
Allows for thin walls, fine details, and integrated components (e.g., hinges, fasteners).
Fewer defects such as porosity and shrinkage.
Fast Production Cycle
Shorter cooling time due to zinc’s thermal properties.
High-speed casting (often up to 200 shots per hour).
Ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
Recyclability
Zinc alloys are fully recyclable with minimal degradation.
Scrap from die casting can be reused efficiently.
Cost-Effective for Medium to High Volumes
Lower tooling costs compared to steel or aluminum molds.
Economical when amortized over large production runs.
FAQ:
Zinc alloy die casting is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten zinc alloy into a mold under high pressure, then cooling it rapidly to form precise and durable metal parts with complex shapes.
Zinc alloy die casting offers:
Excellent dimensional accuracy
Smooth surface finish
High strength and toughness
Fast production cycles
Low energy consumption due to low melting point
Good castability and recyclability
Zinc alloy has a low melting point (≈ 380–420°C), which lowers energy costs, extends mold life, and reduces tool wear. It also offers better mechanical strength and wear resistance than many other die-casting materials.
Zinc alloy die casting is widely used in:
Automotive (e.g., structural parts, emblems)
Electronics (e.g., connectors, housings)
Hardware (e.g., locks, hinges)
Consumer products (e.g., handles, logos)
Zinc die-cast parts can be easily finished with:
Plating (chrome, nickel, etc.)
Painting
Powder coating
The surface finish is smooth (Ra ≤ 1.0 µm) straight out of the mold.
Zinc die casting allows for tight tolerances and complex geometries, with minimal need for post-machining. It's suitable for high-precision components, even with thin walls.
There are two types:
Hot chamber die casting machines (commonly used for zinc)
Cold chamber die casting machines
Each is chosen based on material properties and production needs
Yes. The process supports high-speed casting (up to 200 shots/hour), making it ideal for medium to high-volume production with high repeatability and low per-unit cost.
Yes. Zinc die casting allows for integrated features like:
Threaded inserts
Hinge components
High-strength bearing surfaces
This reduces the need for secondary assembly steps.
Yes. Zinc alloys are fully recyclable with minimal performance loss, and the process allows scrap to be efficiently reused—making it a sustainable and cost-effective choice.