In the field of metal plate cutting, plasma cutting, excellent plasma cutting, has been applied in many industrial fields, but with the development of laser technology such as fiber optics, laser cutting machines have begun to be favored by some users in recent years.
So, which cutting method is more suitable for enterprise product production than plasma and laser cutting?
In this article, we will compare the working principle, scope of use, process, advantages and disadvantages, cost differences, etc., for the future procurement of cutting products and production process design engineers to provide reference.

Working Principle
The working principle of plasma cutting is to use oxygen or nitrogen as the working gas, use the heat of a high-temperature plasma arc to make the metal at the workpiece kerf localized melting and evaporation, and with the momentum of the high-speed plasma flow to exclude the molten metal to form a cutting seam of a processing method.
Laser cutting is produced by the laser beam, through a series of mirrors, and finally by the focusing mirror focused on the surface of the workpiece, in the focal point of the local high temperature, so that the heated point of the workpiece instantaneous melting or vaporization of the formation of the slit.
At the same time, in the process of cutting with auxiliary gas, it will be cut slag blowing out and finally achieve the purpose of processing.
Application
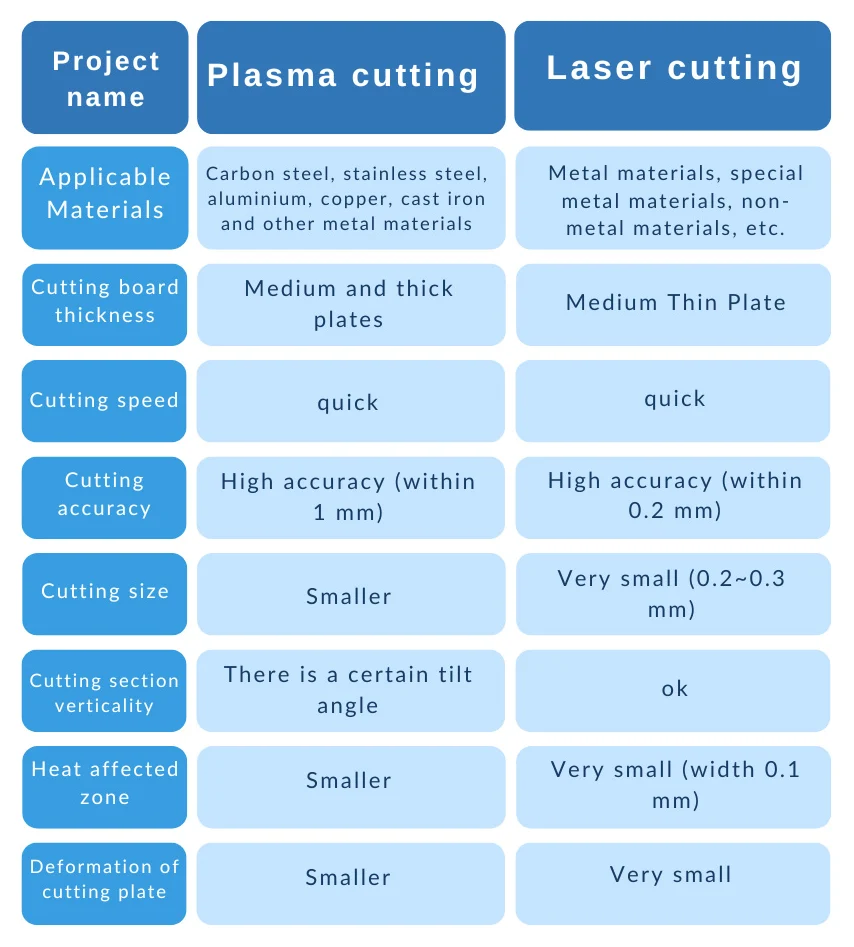
Plasma cutting is suitable for cutting all kinds of metal materials, mainly medium and thick plate cutting. For example, the maximum cutting thickness can be up to 60mm with a plasma cutting of 260 A.
Besides, it can also be used for cutting all kinds of metal materials, such as stainless steel, aluminum, copper, cast iron, carbon steel, and so on. Plasma cutting speed, narrow kerf, and kerf flat allow for low cost, significant energy saving, and economic results.
Laser cutting machine to medium-thin plate, for example, 4000W laser, the maximum can cut about 25mm ordinary carbon steel.
In addition to laser cutting machines for cutting a variety of high melting point materials, heat-resistant alloys, super-hard alloys, and other specialty metal materials, it also cuts semiconductor materials, non-metallic materials, and composite materials.
Laser has hugely high luminous intensity due to its almost non-dispersive directionality. Laser cutting speed, high processing accuracy, narrow slit, compared to plasma cutting heat affected zone is small, cutting plate deformation is small, cutting surface without damage, generally do not need follow-up processing.
In summary, in terms of cutting materials, laser cutting material selection than plasma cutting a wider range; in thin plate cutting, laser cutting has more significant advantages; and in terms of cost, plasma cutting is much cheaper than laser cutting.
Process comparison
Plasma cutting machine can be used for stainless steel, aluminum, copper, cast iron, carbon steel and other metal materials cutting, plasma cutting to medium-thickness plate cutting, 260 A plasma power supply, for example, the maximum cutting thickness of up to 60 mm.
Plasma cutting speed, narrow slit, kerf flat, small heat-affected zone, slight deformation of the workpiece, low operating costs, with significant energy saving and economic results; the disadvantage is that the verticality of the section has a 0.5 ° ~ 1.5 ° angle of inclination, hardening of the cutting section.
Laser cutting is mainly used for medium and thin plates, and the 4000 W laser, for example, can cut ordinary carbon steel of about 25㎜ at the maximum.
In addition to cutting carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloys, and other materials, a laser cutting machine can also be used to cut a variety of high melting point materials, heat-resistant alloys, super-hard alloys, and other unique metal materials, but also cutting semiconductor materials, non-metallic materials and composite materials.
Laser, because of its almost non-dispersive directionality, has a very high luminous intensity, laser cutting speed, high processing accuracy, narrow slit, smooth kerf, small heat-affected zone, slight deformation of the cut sheet, no damage to the cutting surface, generally does not need follow-up processing.
A comparison of the basic process parameters of plasma and laser cutting is shown in Table 1.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The laser cutting machine has some significant advantages over the general cutting method:
① laser cutting slit is small, the cutting surface can be used directly for welding, without grinding.
② Laser cutting machine speed: cutting thin plate speed up to 10m/min, much faster than the speed of a plasma cutting machine.
③ Good cutting quality of laser cutting machine: small deformation, low surface roughness value, small beveling.
④ High precision of laser cutting machine: the positioning accuracy can reach 0.05m m, the repeat positioning accuracy can reach 0.02m m.
⑤ Wide range of cutting materials of laser cutting machine: besides cutting metal, it can also cut wood, plastic, rubber, PVC, leather, textiles, organic glass, and other materials; the scope of application is extremely wide.
Disadvantages of laser cutting:
The high cost of laser cutting, the initial investment, and later maintenance require a high cost; at present, the laser in the cutting of thin plateis cost-effective, but in the cutting of medium-thick plate efficiency is low, unless the quality of the requirements of the higher, otherwise it is not appropriate to use the laser cutting.
Advantages of plasma cutting: in the process of cutting medium-thick plates, it can achieve very high cutting speed, much higher than laser and flame.
The initial investment in equipment is lower than that of laser, and the later maintenance cost is also lower.
Disadvantages of plasma cutting:
① Poor verticality of the cutting surface: a large bevel will be produced on one side of the cutting surface, and the verticality will be poor.
② produces more slag: the cutting process will produce slag under the cutting surface, in order not to affect the quality of the latter process, the slag must be removed by grinding, but also increased labor costs.
③ Harmful gases and arc light will be generated: the principle of plasma cutting determines that harmful dust and arc light will be generated during the cutting process.
However, underwater plasma cutting has been adopted to avoid this defect.
④The consumption of cutting nozzle in the later stage will be more, and the current cutting nozzle is mainly imported, which is more costly.
According to our previous experience, the comparison between laser cutting machine and plasma cutting machine is as follows:
First
The laser cutting machine will not damage the workpiece, while the plasma cutting machine is on the plate.
Still, there is greater or lesser damage, especially in the cutting process of plasma cutting machine cutting gun nozzle problems, which will cause apparent defects on the plate.
Secondly
Because the laser beam is focused on a minimal point of light, the laser cutting machine cuts a narrow slit, plasma cutting machine cuts a slit slightly larger than the laser cutting machine cut.
Third
Laser cutting machine speed: cutting speed up to 10m/min, much faster than the plasma cutting machine.
Fourth
The laser cutting machine cutting surface is smooth, burr-free, good cutting quality, is a non-contact cutting, the cutting edge by the thermal impact is tiny, basically no thermal deformation of the workpiece, altogether avoiding the formation of material punching and shearing of the collapse of the edge, the slit generally do not need secondary processing.
However, the thickness of the cutting plate is limited, and the processing cost is high. And plasma cutting machine according to different models and power size can be cut more than 6 ~ 40mm steel plate, processing costs are relatively inexpensive.
Fifth
The laser cutting machine precision: laser cutting machine positioning accuracy of 0.05 mm, repeat positioning accuracy of 0.02 mm, but the working environment requires high, plasma cutting machine processing accuracy is not as high as the laser cutting machine, but the working environment requirements and mobility is lower, adapt to a broader range of cutting, the skills of the personnel of the water requirements of the relative laser cutting to be low.

Cost comparison:
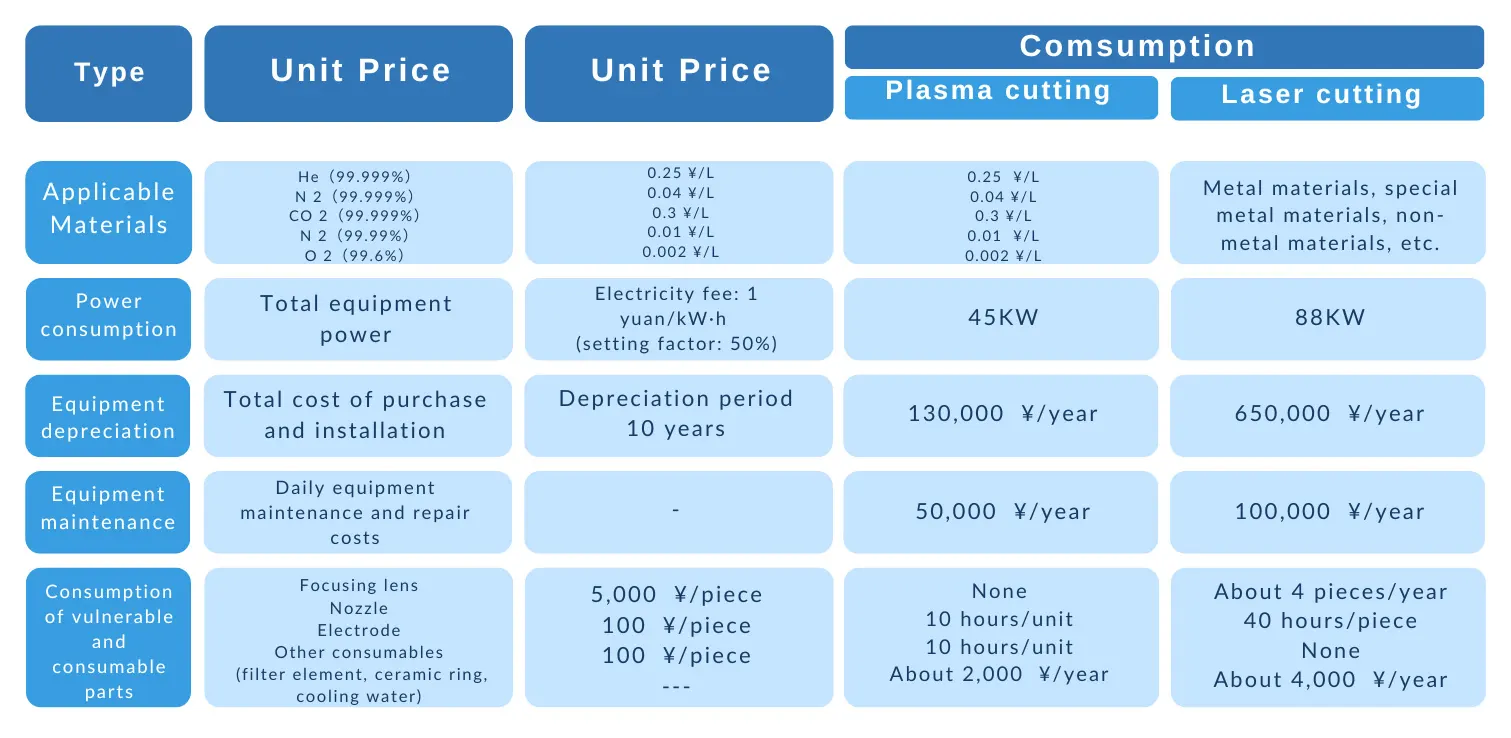
Taking the cutting of a 10 mm ordinary carbon steel plate as an example, the cost analysis of the two cutting processes, plasma cutting, and laser cutting is shown in Table 2.
According to the data analysis in the above table, calculated based on the annual time base of 3,860 h, the running cost of the plasma cutting machine is 97.65 yuan / h, and the running cost of the laser cutting machine is 263.73 yuan / h. The cutting speed of fine plasma cutting and 4 kW laser cutting is 3.4 h / h, respectively.
According to the cutting speeds of fine plasma cutting and 4 kW laser cutting of 3.4 m/min and 1.5 m/min, respectively, the cost of fine plasma cutting is 0.48 yuan/m, and the cost of laser cutting is 2.9 yuan/m.
Comprehensive Comparison and Recommendation
Both plasma cutting and laser cutting have their applicable fields. In addition to cutting carbon steel, stainless steel, and other materials, laser cutting can also be used to cut a variety of high melting point materials, heat-resistant alloys, super-hard alloys, and other unique metal materials, as well as semiconductor materials, non-metallic materials composite materials, the cutting application range is more expansive.
Especially in the case of thin plate cutting, high cutting efficiency, and small thermal deformation, laser cutting has outstanding superiority.
As for the cutting cost, a plasma cutting machine is much cheaper than a laser cutting machine.
To summarize, in the plasma cutting and laser cutting process, selection issues are recommended as follows:
(1) For the general sheet metal cutting field, if the requirement of processing accuracy is not very high, plasma cutting is more cost-effective.
(2) For materials with plate thickness below 6㎜, considering that the thermal deformation of plasma cutting is more significant than that of laser cutting, to prevent the workpiece from colliding with the torch after thermal deformation, plasma cutting is generally not used, and laser cutting or cold punching is used instead.
(3) For all kinds of high melting point materials, heat-resistant alloys, super-hard alloys, and other unique metal materials, as well as semiconductor materials, non-metallic materials, and composite materials, or cutting precision requirements of the thin plate workpiece, it is recommended to use laser cutting.
Development direction:
As the manufacturing technology of laser cutting machines becomes more and more mature, the development direction of high-efficiency laser cutting machines is as follows:
(1) Cutting efficiency to improve further the development of high-efficiency and high-precision CNC laser cutting machines, improve the cutting speed, not only to improve the quality of the beam but also change the cutting process, a more critical aspect is to use a linear motor drive so that it has a more excellent acceleration and moving speed.
(2) Flexible processing of laser cutting Improve the multi-degree of freedom of the laser cutting machine, applicable to the processing of more complex curved surface workpieces.
Developing high-precision fiber laser cutting machines in two-dimensional and three-dimensional aspects of the promotion of the application improves flexible processing.
(3) Increase the width of large thick plate laser cutting Master the long optical range laser transmission technology, thick plate cutting process, high-power laser optical path design and manufacturing technology, and the development of large large thick plate laser cutting equipment.
(4) Intelligent enhancement of cutting machine Further combine the laser with CNC technology, optical technology, and high-precision workpiece positioning, and combine the functional parts of the laser cutting machine with other processing methods to make a multi-functional laser processing machine.
Conclusion
When determining whether plasma or laser cutting is the most suitable method for your application, you must evaluate multiple factors, including the material thickness and type, the precision and edge quality required, the speed at which the process must be completed, and the overall cost implications.
This includes the initial investment in equipment and the long-term expenses, such as power consumption, maintenance, and operational complexity.
Plasma cutting, for instance, is often more cost-effective for thicker materials, while laser cutting delivers exceptional precision on thinner metals and intricate designs.
By carefully weighing these variables, you can select the cutting technology that aligns best with your production goals and budget constraints.



