The insert injection molding process refers to the injection molding process where operators place heterogeneous material inserts in advance.
After positioning the inserts, the injection mold begins to close, and molding continues.
During the molten state, the injection molding material combines with the inserts to form an integrated product.
In the past, the industry primarily applied insert injection molding to nest metal parts. However, as product types and functionality needs have increased, the variety of inserts has gradually expanded to include mesh, glass, wood, coils, metal parts, and more.

Main features
You can fully combine different materials, each with its own characteristics, in the same product to highlight their unique features.
The physical properties of different materials can meet the special performance requirements of some new product designs;
Shorten the product manufacturing process, avoiding a large number of complex assembly operations;
Compared with several direct assembly production mode, insert injection molding makes the reliability of composite products is higher;
Embedding method
Pure artificial placement:
The artificial placement mode is more limited and does not suit large tonnage injection molding machines (generally over 350 tons). It is restricted to producing a small number of simple, small-structured inserted products.
The production efficiency is relatively low, and security is insufficient. As labor costs rise and production safety becomes more necessary, manufacturers have gradually eliminated this mode.
Robot automatic placement:
the mainstream mode of production enterprises, more and more companies are using six-axis robots loaded with mechanical grippers for fully automated placement of inserts, high production beat efficiency, high personal safety protection of employees, mechanical placement of repeated stability and precision are very high, thus ensuring the stability of the batch product quality.
Application and the introduction of examples
Such as in the automotive interior industry, insert injection molding process in the field of automotive interiors are more common, especially in the instrument panel airbag area is more widely used, more models of the instrument panel airbag area applied insert injection molding process, so this paper to specific examples of details to introduce, so that readers can be more physical understanding of the practical application of this special injection molding process type.
As we all know, automotive interior product design must meet the provisions of laws and regulations, but also must meet the host factory for the product function of the design definition.
The mandatory safety performance requirements of the instrument panel airbag area is particularly important, so the insert injection molding process applied in the instrument panel airbag area is often for the technical requirements will be higher to ensure that the normal opening of the instrument panel area in the event of an accident when the airbag burst.
Instrument panel airbag area insert injection molding process application of the main types, currently divided into two categories, integrated insert injection molding and split insert injection molding.
Integrated insert injection molding:
Basic introduction: due to the mesh, nut insert injection molding technology is becoming more mature, the airbag frame and instrument panel integrated insert injection molding has become a trend in the design of instrument panel products.
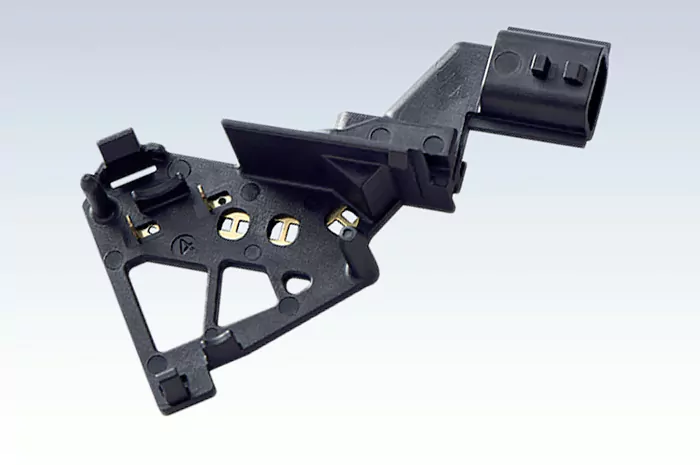
A brand of automobile, the instrument panel is often used in this type of design, the process of the greatest difficulty and the greatest challenge lies in the instrument panel airbag door assembly (see Figure 1, metal screws and mesh welding integration) in the fully automated insert injection molding production process of stability and accuracy.
Fig. 1 The red circle shows three metal screws.
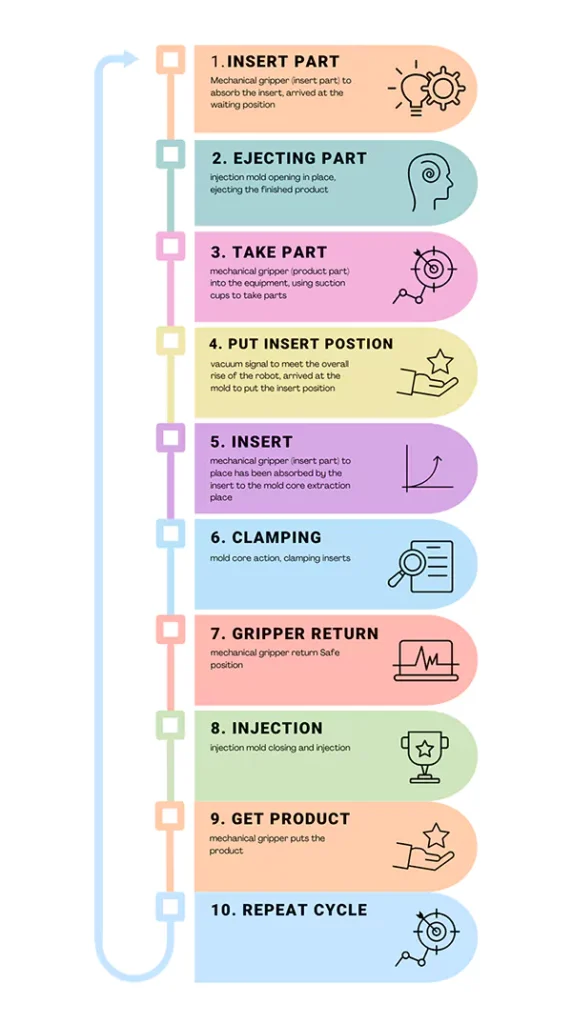
The main process flow (see Figure 2 for schematic):
Mechanical gripper (insert part) to absorb the insert, arrived at the waiting position → injection mold opening in place, ejecting the finished product → mechanical gripper (product part) into the equipment, using suction cups to take parts → vacuum signal to meet the overall rise of the robot, arrived at the mold to put the insert position → mechanical gripper (insert part) to place has been absorbed by the insert to the mold core extraction place → mold core action, clamping inserts → mechanical gripper return Safe position → injection mold closing and injection → mechanical gripper puts the product → repeat cycle.
In order to realize the stability and accuracy of the above said fully automated production, the following three technical details need special attention.
(1) Complexity of Mechanical Gripper Design
In insert molding, an additional step is required to place the insert into the mold cavity, making the gripper design more complex compared to traditional injection molding. The gripper must be capable of handling both the insert placement and the removal of the finished molded product.
For the finished product removal, the design and application are already well-established. Typically, this process involves vacuum suction, clamping fixtures, or a combination of both. There are no significant challenges in this aspect.
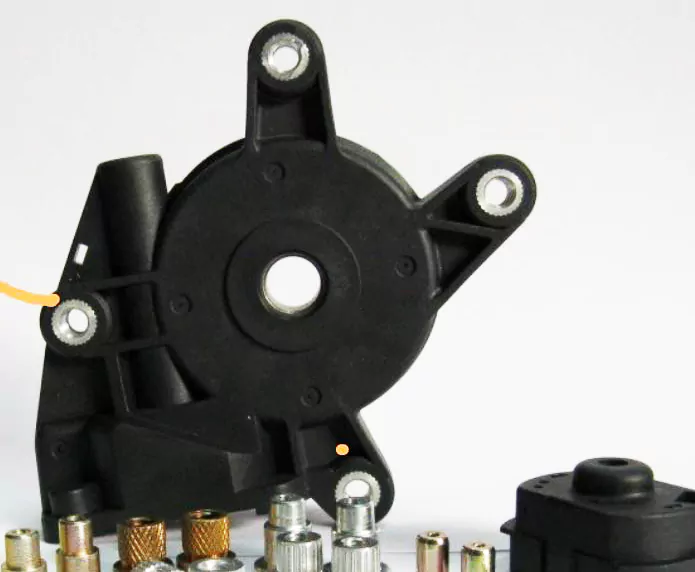
The real complexity lies in the insert handling. Some inserts have a simple structure made of a single material (as shown in Figure 3), while others are complex, multi-material composites (as shown in Figure 4). The design of the gripper must accommodate these variations, making the engineering process more challenging.
(2) for injection molding equipment for repeated mold opening accuracy stability:
As previously introduced, insert injection molding placement accuracy has high requirements of the characteristics of the manipulator are generally selected six-axis robot for the mainstream, can ensure that the realization of the various directions of the flip and flexible movement to achieve.
In the injection molding equipment selection, for insert injection molding process, we must pay attention to the stability of the equipment to open the mold verification study, there has been a specific quantitative data comparison of hydraulic models, Germany KM injection molding machine is generally a more recommended equipment models, after tracking research, KM equipment can ensure that the final actual distance fluctuations in the final stage of the mold at a distance fluctuations in the value of ± 1mm.
Such as the first point above as an example of the problem, insert mesh folding groove in the mold cavity placed in the slot width of 4mm, in order to avoid insert placement deviation, if the equipment to open the mold position fluctuations > ± 2mm, mechanical gripper mesh teeth part of the net basically very easy to hit the mold is damaged, can not be normal continuous production!
In addition, in addition to the selection of suitable models, we also need to not affect the production beat as far as possible under the premise of setting the optimal opening and closing mold equipment reference, not only to ensure the repeatability of the mold opening accuracy, but also does not affect the overall production efficiency.
(3) Trajectory optimization during actual commissioning:
In addition to the above two key details, in the entire robot programming and commissioning phase, it is also necessary to try again and again to determine the optimal trajectory programming, because there are some minor adjustments that can not be completely resolved in the mechanical gripper mechanism or the opening distance adjustment, only through the program trajectory of the refined parameter settings, such as 0.5 ° or 1 ° tilt angle, core extraction set the waiting time and so on. The following are some examples of the types of molds that can be used in the molding process
Split Insert Injection Molding:
This type is the airbag area of the insert design independently, and then subsequently through the welding process, it will be welded to the body of the instrument panel of a process design type, this type is also widely used (Figure 5).
Split Insert Injection Molding Process Characteristics
Compared to integrated insert molding for instrument panels, independent airbag frame insert molding requires significantly lower equipment tonnage. Additionally, it is easier to integrate with highly automated production lines.
Challenges with Integrated Insert Molding
In the insert feeding system, integrated insert molding for instrument panels involves inserts made of different materials, such as mesh fabric and metal rivets.
These inserts often have irregular shapes, making them difficult to stack. As a result, they cannot be fed in bulk and must be manually placed one by one onto positioning fixtures. Precise positioning is required for both the mesh fabric and metal rivets.
Advantages of Independent Airbag Frame Insert Molding
In contrast, independent airbag frame insert molding typically only involves pure mesh fabric. The positioning accuracy can be ensured using just two or three guide holes.
This allows for bulk stacking and automated feeding, simplifying the design of automated feeding systems for engineers.
Advancements in Fully Automated Insert Molding
Currently, the most advanced overseas manufacturing processes utilize fully automated insert molding. This method applies independent airbag frame insert molding with automated bulk feeding of mesh fabric inserts.
A six-axis robot picks up the inserts, places them into the mold cavity, removes the previous molded product, and then closes the mold to continue production. This streamlined process significantly enhances production efficiency.
Full Automation in Automotive Insert Injection Molding
In addition to the multiple types of insert injection molding for instrument panel airbag frame products, insert injection molding applications for other automotive components are increasingly being fully automated. For example, in an electric vehicle being developed, there is a box structure product that requires embedded metal screws.
The process employs vibratory tray sequencing to automatically feed the screws on line, thereby meeting the precise gripping requirements of a mechanical gripper. In this way, the fully automated production of insert injection molding is realized (As shown in Figure 7).
Popularization and application
For some product performance or function above the design of special requirements, insert injection molding will also be accompanied by other special technology composite application.
For example, the insert injection molding at the same time, but also the application of multi-color injection molding process, that is, insert + multi-color composite process type, in the actual new project there are similar cases.

Conclusion
From the basic introduction of the above aspects, it is clear that the insert injection molding process not only has certain requirements for the design structure of the product itself,
but also requires an effective combination of the injection molding machine, mold, and auxiliary equipment, which work together to establish a stable fully automated production system.
This can significantly reduce daily product waste, improve production efficiency, and reduce downtime due to faults.
At the same time, in the context of rising labor costs, businesses are more likely to adopt the fully automated production mode of insert injection molding.