In today’s rapidly developing manufacturing industry, manufacturers have adopted high-precision mold processing technology as a key factor in improving product quality, shortening product manufacturing cycles, and enhancing market competitiveness.
As consumers’ demands for product precision and appearance continue to increase, traditional processing methods no longer meet the needs of modern manufacturing.
High-precision mold processing technology has emerged and developed as an effective solution to this problem.
This paper explores how high-precision mold processing technology is applied in machinery manufacturing, analyzes its key technologies and their impact on the manufacturing process, and verifies its significant effects on improving processing accuracy, enhancing product surface quality, and extending the service life of molds using experimental data.
Breakthrough and Innovation in Precision Milling Technology
Precision milling technology plays a central role in high-precision mold processing.
In recent years, manufacturers have introduced high-speed five-axis linkage machining centers, significantly improving the processing efficiency and accuracy of complex surfaces.
In practical applications, operators use five-axis linkage technology to process a set of automotive lamp molds, reducing processing time by 40% and improving surface roughness to Ra0.2μm.
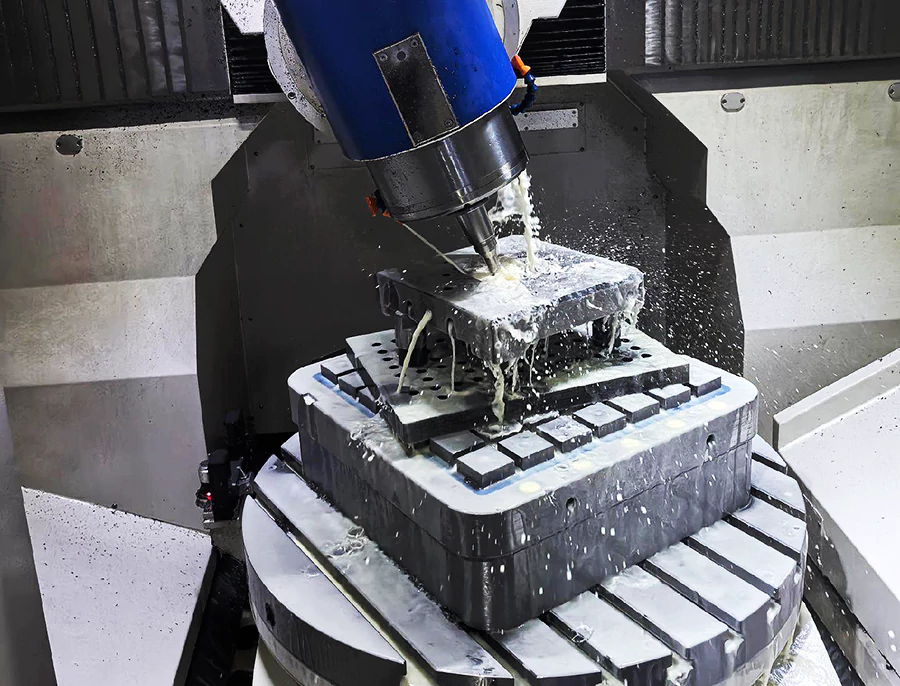

The selection and optimization of superhard cutting tool materials has also advanced significantly.
Experiments reveal that nano-coated cubic boron nitride tools, when used to machine high-hardness mold steel, double the tool life and enhance machining accuracy by 25%.
Furthermore, engineers have made substantial progress in the intelligent regulation of cutting parameters.
By monitoring cutting force and temperature in real-time and automatically adjusting the feed rate and spindle speed, the process ensures machining accuracy and reduces tool wear rate by 30%.
These innovations have greatly enhanced the application of precision milling in mold manufacturing and established a foundation for the rapid production of high-quality molds.
Refinement and Intelligence of EDM Processing
Micro Electrode Design and Manufacturing
Engineers design and manufacture micro electrodes as the core of EDM refinement.
In practice, operators employ a multi-step precision machining method to produce microfine electrodes.
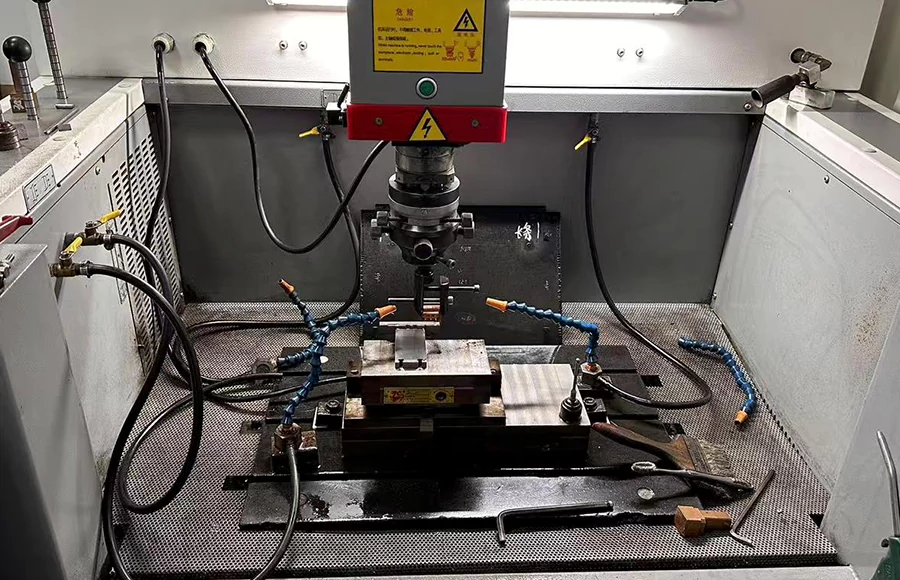
First, they rough-machine the electrode material (e.g., copper-tungsten alloy) using a high-precision five-axis CNC machine tool to form a basic contour.
Then, they finish the electrode with microfabrication technology to achieve surface roughness below Ra0.05μm.
To enhance wear resistance and electrical conductivity, they apply a 2-3 μm thick nanoscale titanium alloy coating to the electrode surface.
For geometric design, engineers combine CAD software with FEA to optimize the electrode shape.
For example, when machining deep grooves, they use a ‘stepped’ electrode with each step 0.2mm wide and 0.5mm high, improving coolant flow efficiency and reducing wear.
In micro-hole machining, they utilize hollow electrodes with an inner diameter of 0.05mm and an outer diameter of 0.1mm to balance precision and waste discharge.
These methods reduce electrode diameters to 0.01mm, significantly enhancing machining precision and efficiency.
Adaptive Control of Discharge Parameters
Technicians dynamically adjust discharge parameters during EDM refinement and intelligence.
By monitoring voltage and current in the machining gap in real-time, the system adjusts discharge energy, pulse width, and frequency dynamically.
In experiments involving high-temperature alloy mold machining, engineers increased machining efficiency by 25% and reduced surface roughness to Ra0.8μm by implementing adaptive control technology.
The intelligent control algorithm automatically selects optimal parameter combinations according to the machining stage, effectively preventing short-circuits and arc-breaks.
For example, operators use high-energy, low-frequency discharge during roughing and shift to low-energy, high-frequency settings for finishing.
This strategy not only enhances machining accuracy but also extends electrode life, reducing the electrode wear rate by 30% in a 200-hour continuous machining test.
With machine learning algorithms, the system continuously optimizes parameter selection to further improve results.
EDM Strategy for Complex Surfaces
To address precision control challenges for complex surfaces, engineers developed an adaptive trajectory planning algorithm.
The algorithm adjusts the electrode feed path and speed dynamically based on the surface’s geometric characteristics, minimizing overcutting and undercutting.
In automotive mold machining experiments, engineers reduced surface contour errors by 40% to ±0.005mm by employing this strategy.
They improved efficiency by applying multi-electrode co-processing technology, which reduced overall time by 35% by allocating tasks among 3-5 electrodes to process different areas simultaneously.
Electrode compensation technology adjusted feed rates according to real-time wear measurements, maintaining stable machining accuracy.
A 50-hour continuous surface machining test controlled final contour accuracy deviation within ±0.003mm.
Application of Laser Processing Technology in Mold Manufacturing
Ultra-short Pulse Laser Micromachining
Manufacturers use ultrashort pulse laser micromachining technology to achieve submicron-level precision in mold manufacturing.
Femtosecond lasers enable the creation of micron-sized fine structures on mold surfaces.
Experiments demonstrate that a laser with a wavelength of 1064 nm and a pulse width of 200 fs can process mold steel to create microgrooves with a minimum line width of 2 μm and a depth-to-width ratio of up to 20:1.
This technology is especially suitable for producing micro-injection molds, such as those used for mobile phone camera lenses.
In one case, laser processing reduced mold surface roughness to Ra0.05μm, an 80% improvement over conventional methods.
Additionally, the small heat-affected zone prevented material deformation and micro-cracks, extending mold service life.
This technology also supports direct processing of three-dimensional microstructures, opening new possibilities for complex functional surfaces.
Laser Surface Treatment and Peening
Engineers significantly improve mold wear resistance and service life through laser surface treatment and peening.
Rapid heating and cooling during laser quenching form hardened layers up to 0.5-2mm thick on mold surfaces.

Experimental data indicate that laser-quenched mold steel’s surface hardness increased from HRC45 to HRC62, tripling wear resistance.
Laser cladding deposits high-hardness, corrosion-resistant alloy layers onto mold surfaces.
In a die-casting mold strengthening experiment, engineers extended mold life by 2.5 times using Ni-based alloy powder laser cladding to form a 0.8mm thick reinforced layer.
Laser surface texturing, which creates micron-sized regular structures, improved mold release performance and product surface quality.
Laser-EDM Process
The laser-EDM process combines the strengths of both technologies to enhance efficiency and precision.
Engineers begin by roughing with a laser to remove material quickly and finish with EDM to achieve high-precision surfaces.
In experiments, the composite process reduced total machining time by 45% compared to EDM alone while maintaining accuracy within ±0.005mm.
Laser pre-treatment improved EDM discharge conditions, increasing machining stability. Surface roughness reached Ra0.2μm, a 60% improvement over traditional EDM.
Comprehensive Benefit Analysis of High-Precision Mold Processing Technology
Improvement of Machining Accuracy and Surface Quality
High-precision mold processing technologies, including ultra-short pulse lasers, precision milling, and EDM, have enabled micron and submicron-level machining accuracy.
Combining these technologies reduces mold surface roughness to Ra0.2μm or lower.
Experimental data reveal that these advancements improve shape error control to within ±2μm and enhance surface roughness by over 50%, directly benefiting product performance and appearance.
Extension of Mold Life and Cost Reduction
High-precision machining extends mold life and reduces production costs.
Enhanced wear and corrosion resistance, achieved through precision machining and surface treatments, doubled average mold life.
Reduced maintenance needs further lowered downtime and repair costs.
For instance, an automotive parts manufacturer increased mold life from 500,000 to 1.2 million stampings, reducing costs by 40%.
Shortening Product Development Cycles
High-precision technologies shorten product development cycles by achieving greater accuracy in fewer iterations.
Using five-axis linked machining centers and intelligent design systems, companies reduced mold development times by 40%, enabling faster product launches.
A consumer electronics manufacturer reduced time-to-market from six months to 3.5 months, enhancing market responsiveness and competitiveness.
Conclusion
The adoption of high-precision mold processing technology in machinery manufacturing has driven process innovation, significantly improving product quality and production efficiency. Precision milling, EDM, and laser processing collectively address high-precision requirements for complex shapes.
Experimental results confirm that these technologies improve mold accuracy by over 30%, reduce surface roughness to the nanometer level, and extend mold life by 2-3 times.
As digital and intelligent technologies continue to integrate, high-precision mold processing will further enhance the manufacturing industry’s quality and efficiency, supporting product innovation and industrial upgrades.
What is high-precision machining, and why is it essential in mold processing?
High-precision machining involves using advanced tools and techniques to achieve exceptional accuracy and surface quality in manufacturing molds. It is essential to meet the increasing demand for high-quality, complex products in industries like automotive, electronics, and aerospace.
What role does precision milling play in mold processing?
Precision milling allows for efficient and accurate machining of complex surfaces, such as automotive molds. Modern five-axis linkage machining centers enhance accuracy and reduce processing time significantly.
How does EDM contribute to high-precision mold manufacturing?
EDM refines the machining of intricate mold components, enabling precision shaping of materials with high hardness. Advanced control systems optimize discharge parameters, improving accuracy and reducing surface roughness.
What advancements have been made in EDM microelectrode technology?
Engineers now use techniques like nanoscale coating and optimized geometric designs to create durable and efficient microelectrodes. These electrodes improve precision, especially in micro-hole and deep-groove machining.
What are the key innovations in cutting tool technology for mold processing?
Innovations include the use of superhard materials like cubic boron nitride with nano-coatings. These tools enhance tool life and improve machining accuracy when working with tough mold materials.
How does real-time parameter adjustment improve machining accuracy?
Real-time monitoring of machining parameters, such as cutting force and temperature, ensures optimal feed rates and spindle speeds, resulting in reduced tool wear and enhanced precision.
How do multi-electrode co-processing methods benefit mold manufacturing?
Multi-electrode co-processing enables simultaneous machining of different areas of a mold, significantly reducing overall processing time while maintaining accuracy.
What is the significance of surface roughness in high-precision mold processing?
Surface roughness determines the quality and performance of the final product. High-precision machining technologies achieve lower surface roughness values, such as Ra0.2μm, ensuring superior product finishes.